Strategies for a Flat Stomach : Unveiling the Truth About Belly Fat
The science behind it
Understanding the Basics of Belly Fat and Impact of Belly Fat on Health
When it comes to achieving a flat stomach, it’s essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the factors contributing to the accumulation of belly fat. While many people aspire to have a toned midsection for aesthetic reasons, it’s important to recognize that belly fat goes far beyond mere appearance. Excess abdominal fat can have a significant impact on overall health and increase the risk of various diseases. In this article, we will delve into the causes and types of belly fat, the health risks associated with it, and reveal effective strategies for banishing belly fat and achieving a flat stomach.
Causes of Belly Fat
A. Overeating and Excess Caloric Intake
B. Poor Diet and Unhealthy Food Choices
C. Sedentary Lifestyle and Lack of Physical Activity
D. Hormonal Imbalances and Menopause
E. Genetics and Body Composition

Belly fat can stem from various factors, including overeating and consuming an excessive number of calories. When we consistently consume more calories than our bodies need, the excess is stored as fat, often accumulating in the abdominal region. Additionally, a poor diet characterized by unhealthy food choices, such as processed and sugary foods, can contribute to belly fat. Leading a sedentary lifestyle with minimal physical activity also plays a significant role in the accumulation of excess abdominal fat. Hormonal imbalances, particularly during menopause, can affect fat distribution and lead to an increase in belly fat. Furthermore, genetics and body composition can influence the propensity to store fat in the abdominal area.
Types of Belly Fat
A. Subcutaneous Fat: The Visible Enemy
B. Visceral Fat: The Hidden Peril
There are two primary types of belly fat: subcutaneous fat and visceral fat. Subcutaneous fat is the visible fat that lies just beneath the skin. It can be pinched and felt, often leading to frustration and self-consciousness. On the other hand, visceral fat is the fat that accumulates deep within the abdominal cavity, surrounding vital organs. While not visible to the naked eye, visceral fat poses a more significant health risk. It has been associated with various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and metabolic syndrome.
Health Risks Associated with Belly Fat
A. Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
B. Impact on Insulin Sensitivity and Diabetes
C. Influence on Hormone Regulation and Imbalance
D. Connection to Metabolic Syndrome
Excess belly fat is not just a cosmetic concern; it poses significant risks to our health. One of the most notable risks is an increased likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease and stroke. Belly fat contributes to inflammation and releases hormones that can negatively impact insulin sensitivity, potentially leading to the development of type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, the accumulation of belly fat can disrupt hormone regulation, leading to imbalances that may affect metabolism and overall health. This interplay between hormones, insulin, and metabolism can contribute to the development of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that heighten the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Easy Strategies for a Flat Stomach
How Fat Stores Are Utilized as Energy
Belly fat, often considered a troublesome area, is a common concern for many individuals striving to achieve a flat stomach. To gain a better understanding of how to tackle this issue, it is important to comprehend how fat stores are utilized as energy within our bodies.

Our bodies store excess energy in the form of fat, specifically in adipose tissue located around the abdomen. When our energy expenditure exceeds our intake, our body taps into these fat stores to provide the necessary fuel. This is known as fat metabolism.
To break down stored fat, our body undergoes a process called lipolysis. Enzymes called lipases are responsible for this process, breaking down triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol. These fatty acids are then released into the bloodstream, transported to various tissues, and utilized as a source of energy.
The Role of Hormones in Fat Metabolism
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating fat metabolism, including the breakdown and utilization of stored fat. One hormone in particular, called insulin, has a significant impact on abdominal fat accumulation.
Insulin is secreted by the pancreas in response to elevated blood sugar levels. Its primary function is to facilitate the uptake of glucose by cells, promoting energy storage. However, when insulin levels are consistently high, it can promote the storage of excess calories as fat, particularly in the abdominal region.
On the other hand, hormones such as glucagon, growth hormone, and adrenaline have an opposing effect to insulin. They work together to stimulate lipolysis and increase the utilization of stored fat for energy. By keeping these hormones in balance, we can optimize our body’s ability to metabolize belly fat.
Importance of Caloric Deficit for Losing Belly Fat
Creating a caloric deficit is a fundamental aspect of shedding belly fat and achieving a flat stomach. This deficit occurs when we consume fewer calories than our body needs, forcing it to utilize stored energy, including fat.
It is important to note that a moderate caloric deficit is key for sustainable and healthy weight loss. Severely restricting calories can lead to muscle loss, metabolic slowdown, and nutrient deficiencies. To strike the right balance, it is recommended to aim for a deficit of around 500 to 1000 calories per day, depending on individual needs.
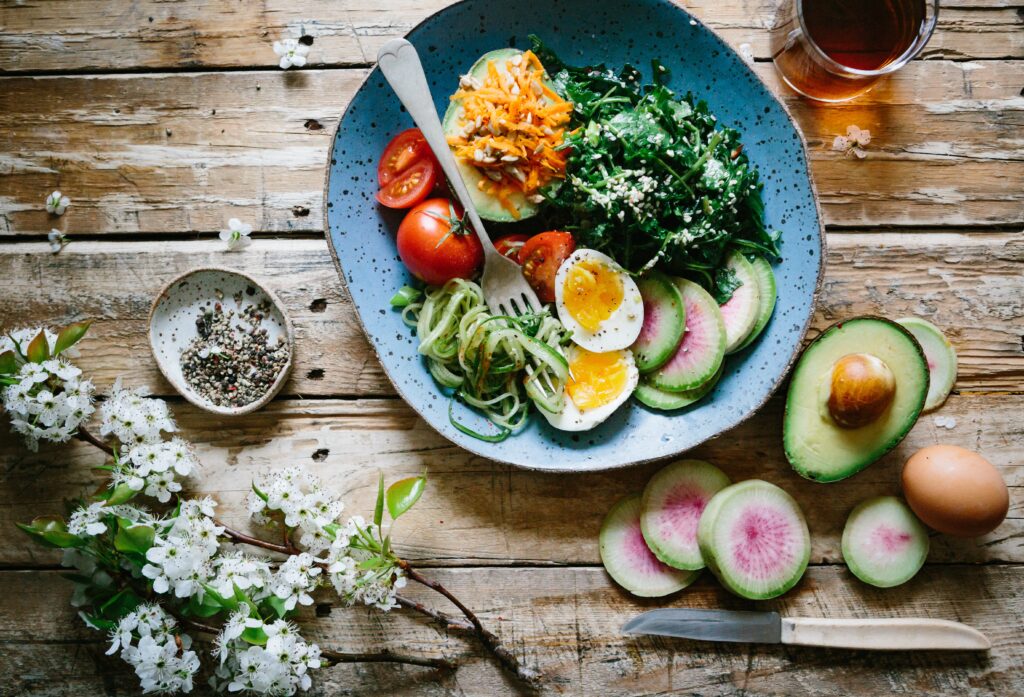

In addition to a caloric deficit, emphasizing a nutrient-dense, balanced diet is essential. Incorporating whole foods, such as lean proteins, fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, and healthy fats, can provide the body with necessary nutrients while promoting satiety.
Combining a caloric deficit with regular physical activity further enhances belly fat loss. Engaging in a combination of cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and targeted abdominal exercises can help increase energy expenditure, build lean muscle, and promote a toned midsection.
Conclusion
By understanding the inner mechanisms of fat metabolism, the influence of hormones, and the significance of a caloric deficit, one can adopt effective strategies to achieve a flat stomach and reduce stubborn belly fat. Remember, consistency, balanced nutrition, and regular physical activity are crucial components of this journey towards a healthier and more confident you. Embrace these easy strategies and unveil the truth about belly fat for a flatter and happier stomach.
Key Take aways
Can targeting abdominal exercises alone help in reducing belly fat?
Targeting abdominal exercises alone is not sufficient for reducing belly fat. While abdominal exercises can help strengthen and tone the muscles in the abdominal area, they do not specifically target or reduce fat in that region. The concept of spot reduction, which means losing fat in a specific area of the body through targeted exercises, is a common misconception.
To reduce belly fat effectively, it is essential to focus on overall body fat loss through a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and a balanced lifestyle. Here are some key points to consider:
1.Caloric deficit: To lose fat, including belly fat, you need to create a caloric deficit by consuming fewer calories than you burn. This can be achieved through a combination of healthy eating and increased physical activity.
2.Cardiovascular exercise: Engaging in aerobic exercises like running, swimming, cycling, or brisk walking can help burn calories and promote overall fat loss, including abdominal fat. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
3.Strength training: Incorporating strength training exercises into your routine can help increase muscle mass and boost your metabolism. This can lead to greater overall fat burning, including belly fat. Compound exercises such as squats, deadlifts, lunges, and chest presses are effective for building muscle and burning calories.
4.Balanced diet: Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial for fat loss. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid or limit foods high in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates.
5.Consistency and patience: Losing belly fat and achieving a healthy body composition takes time and dedication. It’s important to maintain consistency with your exercise routine and dietary habits. Results may not be immediate, but with persistence and patience, you will see progress over time.
Remember, while abdominal exercises can help strengthen and define the muscles in that area, they are just one part of a comprehensive approach to reducing belly fat. By combining targeted exercises with a healthy lifestyle, you can work towards achieving your goals effectively.
Is it possible to lose belly fat without following a strict diet?
While following a strict diet can be helpful for losing belly fat, it is possible to make progress without adhering to an overly restrictive eating plan. The key is to focus on creating a sustainable and balanced approach to your eating habits. Here are some strategies to consider:
1.Portion control: Pay attention to your portion sizes and practice mindful eating. Be aware of your body’s hunger and fullness cues, and aim to eat until you’re satisfied rather than overly full.
2.Balanced meals: Include a combination of lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates in your meals. This can help keep you satiated and provide essential nutrients without feeling deprived.
3.Choose nutrient-dense foods: Opt for whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet. These foods tend to be lower in calories while providing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
4.Mindful eating: Slow down while eating, savor each bite, and pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness signals. This can help prevent overeating and promote a healthier relationship with food.
5.Reduce sugary and processed foods: Minimize the intake of sugary beverages, desserts, processed snacks, and foods high in added sugars. These can contribute to belly fat and overall weight gain.
6.Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Staying hydrated can help support your metabolism and prevent overeating, as thirst can sometimes be mistaken for hunger.
7.Regular physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise, including cardiovascular activities and strength training, can aid in burning calories and promoting overall fat loss, including belly fat. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises at least twice a week.
By adopting these habits and making sustainable changes to your eating patterns, you can make progress in losing belly fat without strictly following a restrictive diet. The key is to find a balanced approach that works for you and supports your long-term health and well-being.
How long does it take to see visible results in reducing belly fat?
The time it takes to see visible results in reducing belly fat can vary depending on various factors, including your starting point, genetics, diet, exercise routine, and overall lifestyle. It’s important to note that losing fat, especially in specific areas like the belly, is a gradual process that requires consistency and patience. Here are some general considerations:
1.Initial changes: In the first few weeks of adopting a healthier lifestyle, such as incorporating regular exercise and making dietary changes, you may start to notice some initial changes. This could include feeling more energized, improved digestion, and potentially some weight loss.
2.Body composition changes: As you continue with your healthy habits, your body composition will gradually change. This means that you may be losing fat while simultaneously gaining muscle, which can impact your overall appearance. Building muscle can help increase your metabolic rate and promote fat loss, including belly fat, over time.
3.Timeframe: It’s difficult to provide an exact timeframe as everyone’s body is different. Generally, it’s realistic to expect noticeable changes in belly fat reduction within a few months of consistently following a balanced diet and exercise routine. However, keep in mind that the rate of fat loss can vary. It’s important to focus on sustainable progress rather than expecting immediate or drastic changes.
4.Consistency is key: To see significant and lasting results, consistency is crucial. Stick to your healthy habits, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, for an extended period. Remember that healthy and sustainable weight loss typically occurs at a rate of 1-2 pounds (0.5-1 kg) per week.
It’s essential to approach your journey to reduce belly fat with a long-term mindset. Rather than solely focusing on visible results, celebrate the non-scale victories, such as improved energy levels, increased strength, better sleep, and enhanced overall well-being. Stay committed to your healthy habits, and over time, you’ll likely see the desired changes in your belly fat and overall body composition.
Are there specific foods that can help in burning belly fat?
While specific foods cannot directly target and burn belly fat, incorporating certain foods into your diet can support overall weight loss and contribute to a healthier body composition. These foods tend to be nutrient-dense, high in fiber, and have properties that can aid in appetite control and metabolism. Here are some examples:
1.Protein-rich foods: Consuming adequate protein can help increase satiety, reduce cravings, and support muscle growth and repair. Good sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and tofu.
2.Fiber-rich foods: High-fiber foods can promote feelings of fullness, regulate digestion, and stabilize blood sugar levels. Examples of fiber-rich foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts.
3.Healthy fats: Including sources of healthy fats in your diet can help promote satiety and support overall health. Choose foods rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon.
4.Green tea: Green tea is often associated with metabolism-boosting properties due to its catechin content, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). While the effects may be modest, incorporating green tea as part of a balanced diet can be beneficial.
5.Spices and herbs: Certain spices and herbs, such as ginger, turmeric, cayenne pepper, and cinnamon, may have potential thermogenic effects, helping to slightly increase metabolism and aid in weight management.
6.Water-rich foods: Foods with high water content, like cucumbers, watermelon, and leafy greens, can help keep you hydrated and contribute to feelings of fullness with fewer calories.
It’s important to note that while these foods can support a healthy diet and weight loss, they are most effective when part of an overall balanced and calorie-controlled eating plan. Remember that a holistic approach that combines a nutritious diet with regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle is key for achieving and maintaining a healthy body composition.
What are some effective ways to track progress in losing belly fat?
Tracking your progress in losing belly fat can help you stay motivated and make adjustments to your approach if needed. Here are some effective ways to track your progress:
1.Measurements: Take regular measurements of your waist circumference using a measuring tape. Measure around your waist at the level of your navel. Tracking changes in waist circumference can provide a tangible measurement of belly fat loss over time.
2.Body weight: While weight alone is not the most accurate indicator of belly fat loss, tracking your overall body weight can still be useful. Weigh yourself regularly, preferably at the same time of day and under consistent conditions. Remember that weight can fluctuate due to factors like water retention, so focus on trends over time rather than day-to-day fluctuations.
3.Body composition analysis: Consider getting a body composition analysis done periodically. This can provide valuable information about your fat mass, muscle mass, and overall body composition. Techniques such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans, bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), or skinfold caliper measurements can give you a more detailed understanding of changes in your body fat percentage.
4.Progress photos: Take photos of your belly area at regular intervals. Comparing photos side by side can reveal subtle changes in body shape and help you notice progress that may not be evident on the scale.
5.Clothing fit: Pay attention to how your clothes fit. Notice if your pants or belts feel looser around the waist. This can be a good indication that you are losing belly fat even if the scale doesn’t show a significant change.
6.Physical performance: Monitor improvements in your physical performance and fitness level. Notice if you’re able to perform exercises with greater ease or if you have more endurance during your workouts. These improvements indicate that your body composition is changing, even if you don’t see immediate visible changes.
Remember, progress in losing belly fat may not always be linear, and it’s normal to experience plateaus or slower progress at times. Focus on the overall trend of your measurements and keep in mind that sustainable fat loss takes time. Be patient and consistent with your efforts, and use these tracking methods as tools to stay motivated and make informed adjustments along the way.